Prometryn – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/14/2017 / By Janine Acero

Prometryn is a herbicide used for control of several annual grasses such as foxtail, wild oats, millets, ryegrass and goosegrass; and broadleaf weeds including dandelion, chickweeds, nightshade and deadnettle.
Prometryn is applied on crops such as cotton, celery, pigeon peas and dill, and it is formulated as a “single active ingredient in wettable powder, crystalline, and flowable concentrate.”
Prometryn was first registered in the U.S. in 1964, and it has the molecular formula of C10H19N5S.

List of known side effects
Prometryn may be harmful if inhaled, and is hazardous to aquatic ecosystems with long-term effects.
The open chemistry database PubChem classified prometryn as Group E “Evidence of Non-carcinogenicity for Humans”. Data collected from animal studies showed that prometryn is non-toxic in oral, dermal and inhalation routes. It is also considered slightly to non-toxic for the eyes.
However, the pesticide information profile released by the Pesticide Management Education Program noted that prometryn may be slightly to moderately toxic. Like any chemical, it is harmful if swallowed and “exposed workers may complain of sore throat and nausea.”
Body systems affected by prometryn
Herbicides like prometryn are used for weed control, inhibiting the amino acid synthesis in plants. This pathway are not found in mammals, which makes prometryn and other related herbicides practically non-toxic to animal models in studies. However, long-term exposure in animal studies showed that prometryn may target organs including the liver, kidneys, and bone marrow.
Items that can contain prometryn
Prometryn can be applied to a number of crops including carrots, celery, cotton, dill, peanuts, pigeon peas, potatoes and sunflowers.
How to avoid prometryn
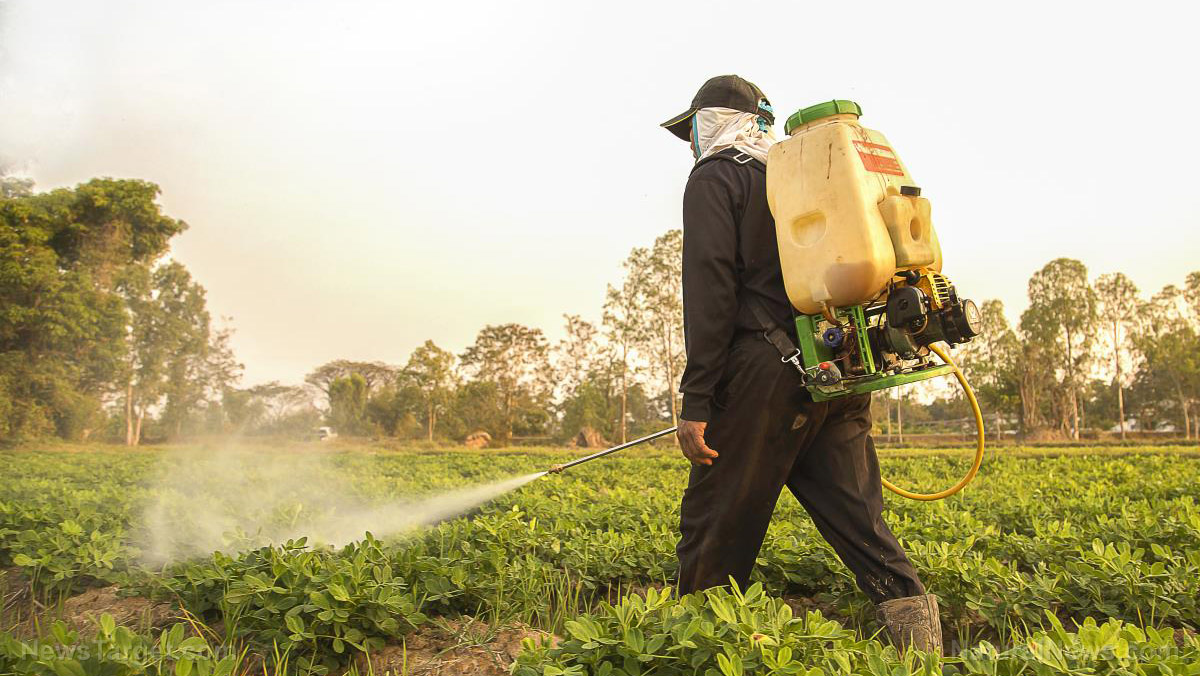
Prometryn handlers and applicators are the most prone to exposure to this substance. Avoid eye and skin contact by wearing protective gear (tightly sealed goggles and chemical-resistant gloves). Avoid inhalation of its fumes and contamination of food and feed. Wash thoroughly after handling.
Where to learn more
Summary
Prometryn is a herbicide used for control of grasses and weeds in a number of crops such as celery, cotton, dills and pigeon peas.
Prometryn may be harmful when inhaled, but is generally non-toxic to the eyes and skin. However, precautionary measures such as wearing protective gear are still required, especially for handlers, mixers and applicators of this chemical.
Prometryn is classified as not carcinogenic to humans, but may be harmful to organs such as liver, kidneys, and bone marrow in long-term exposures.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: