Tribenuron-methyl — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/17/2017 / By Earl Garcia

Tribenuron-methyl is classified as a selective systemic herbicide that is used to protect staple crops and cereals — such as oats, rye, wheat and triticale — and effectively eliminate a wide variety of annual and perennial weeds including:
- Thistle
- Dock
- Curl sorrel
- Yarrow
- Milk thistle
- Plantain
- Dandelion
- Horsetail
- Buttercup
- Coltsfoot
An entry posted on the AgChem Access website notes that the herbicide works by mitigating amino acid synthesis in weeds, which then inhibits cell division and cell growth.

List of known side effects
An article posted on the Pesticide Action Network North America (PANNA) website reveals that tribenuron-methyl exposure may cause reproductive and developmental toxicity, neurotoxicity, and acute toxicity. Likewise, the entry stresses that inhaling the harmful herbicide may trigger the onset of various respiratory woes such as moderate emphysema, coughing, and shortness of breath.
The toxic substance is also associated with a host of digestive conditions. According to the article, exposure to the harmful chemical may result in nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea as well as more serious issues such as electrolyte depletion, protein metabolism disturbance, and significant weight loss. The hazardous compound is also known to target the central nervous system and induce severe headache and confusion. Likewise, the herbicide is shown to cause skin and eye irritation.
An entry featured on the open chemistry database Pub Chem notes that the systemic herbicide may pose a threat to environmental health as well. According to the article, tribenuron-methyl may contaminate water ways and negative affect aquatic animals and resources.
Body systems affected by tribenuron-methyl
Tribenuron-methyl is notoriously hazardous to the respiratory tract. Likewise, the harmful chemical is known to target both the digestive tract and the central nervous system. The systemic herbicide is also found to affect both eye and skin health.
Items that can contain tribenuron-methyl
Tribenuron-methyl is the key component of commercially available herbicides across the U.S. The herbicide can be used in both 50 and 70 percent solutions, and may also come in various formulations such as water dispersible granules.
How to avoid tribenuron-methyl
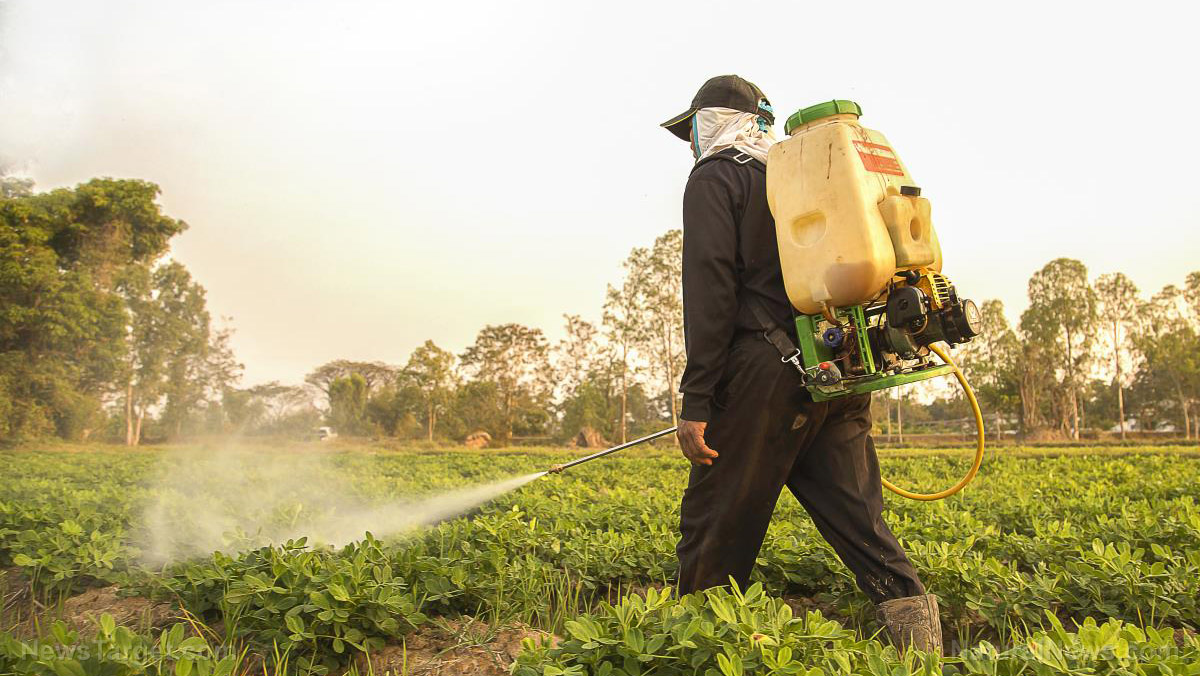
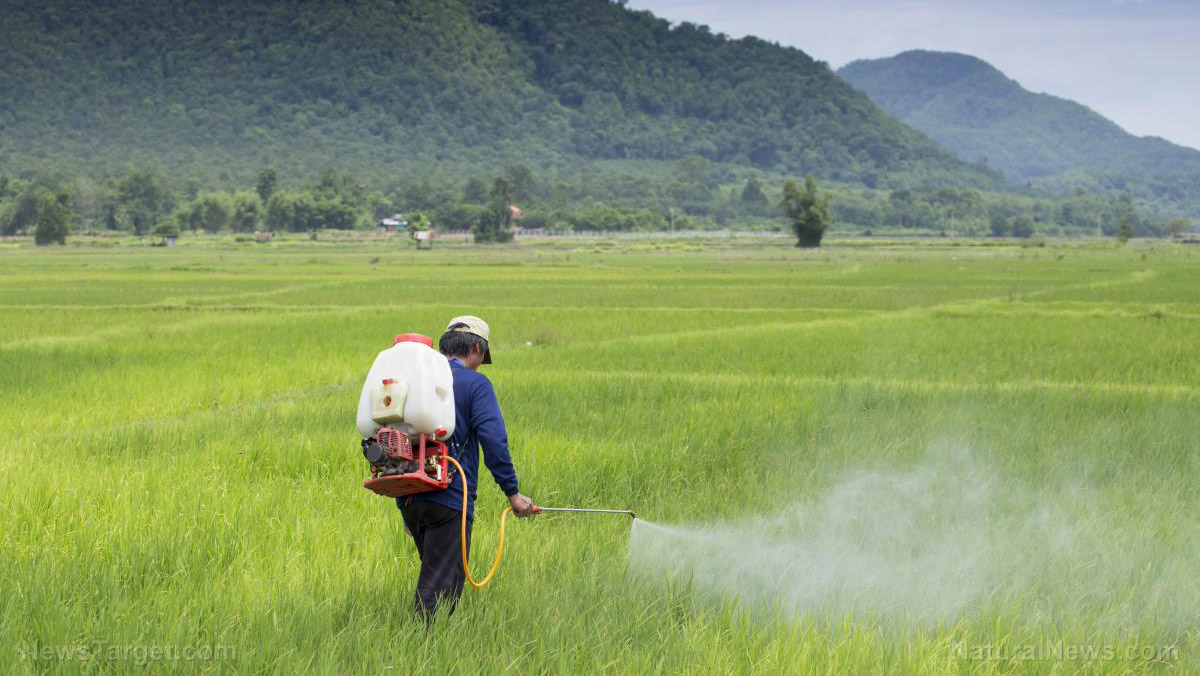
A safety data sheet published by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends that workplaces install adequate ventilation to prevent workers from inhaling toxic fumes. Likewise, pesticide users are advised to wear breathing equipment and protective gloves and clothing to mitigate the risk of inhalation and direct skin and eye contact.
The guidelines also highlight the importance of routine hand washing to prevent the chemical from entering the digestive tract. Furthermore, the safety data sheet recommends that people who inhaled toxic fumes go to an area with fresh air. Victims are also advised to thoroughly wash the eyes and skin following direct contact.
Where to learn more
- Glyphosate and cancer: Read how this deadly weed killer promotes multiple myeloma, leukemia, sperm damage, infertility, kidney damage, autism, endocrine disruption, DNA damage and birth defects
- Researchers struggle to find effective way to mitigate damage done by atrazine, a common weedkiller known to harm human health, wildlife, aquatic life
- Weed killer found contaminating most popular US foods, including many non-GM products
- All 8 extreme childhood food allergies are also common ingredients in CDC-recommended vaccines… coincidence?
- Tomatoes, dandelions, and hawthorn – why they trump Obamacare
Summary
Tribenuron-methyl exposure results in reproductive and developmental toxicity, neurotoxicity, and acute toxicity.
Tribenuron-methyl may trigger the onset of moderate emphysema, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Tribenuron-methyl may cause electrolyte depletion, protein metabolism disturbance and significant weight loss.
Tribenuron-methyl raises the odds of severe headache, confusion, and skin and eye irritation.
Tribenuron-methyl is particularly detrimental to the respiratory system’s overall health.
Tribenuron-methyl exposure may also harm both the digestive tract and the central nervous system.
Tribenuron-methyl negatively affects both skin and eye health.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: