Pesticides – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/18/2017 / By Frances Bloomfield

Pesticides are chemicals or substances used to control, repel, or eliminate pests. These organisms can invade or damage crops and homes, and may even cause harm to humans or other animals. Due to the wide variety of pests, there is an equally diverse range of pesticides, with the most common ones being:
- Insecticides: These are pesticides intended to reduce the destruction caused by insects and their eggs.
- Rodenticides: Similar to insecticides but meant for rodents, these pesticides are used to decrease rodent populations and minimize exposure to rodent-borne disease.
- Herbicides: More commonly known as “weed killers”, herbicides are used to destroy weeds and improve crops.
- Fungicides: These are utilized for the protection of crops and seeds from fungi like mold and mildew.
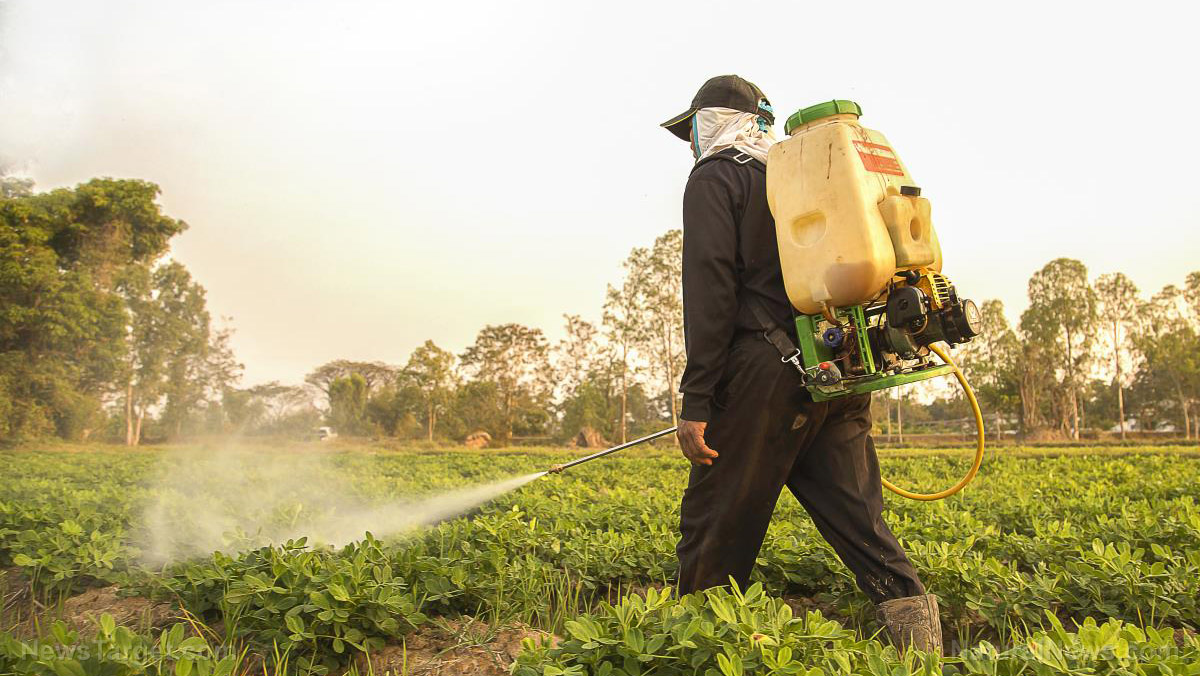
The U.S. government agency responsible for licensing and registering all pesticides is the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which has registered over 865 pesticides that are available in thousands of pesticide products. Outside of the EPA, there are many more government and non-government entities that monitor and scrutinize the plethora of commercially available pesticides.
Despite the prevalence of pesticides in agricultural applications, pesticides have been the subject of controversy for years. This is largely because numerous health problems the world over have been linked to the use of all kinds of pesticides.

List of known side effects
Organophosphates and carbamates are two kinds of synthetic pesticides that have the same mechanism of action: they both target the nervous systems of insects. Acute exposure to either substances can cause the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, which in turn leads to the buildup of acetylcholine. Excessive acetylcholine has been found to result in nausea, diarrhea, hypotension or low blood pressure, fatigue, and increased salivation and perspiration. In addition, Toxipedia.org has noted that some organophosphates have been known to cause delayed neurological reactions which manifest as muscle weakness in the legs and arms.
Similar to organophosphates and carbamates, pyrethroids affect the nervous system as well. These pesticides have been shown to cause aggressiveness, tremors, and seizures upon acute dermal exposure. In addition, some pyrethroids can elicit allergic skin reactions, while others are said to increase the risk for cancer and defects of the reproductive and/or endocrine systems.
Organochlorines are a type of pesticide that have been banned or heavily restricted due to the potential negative effects on the environment. If ingested, organochlorines can bring about nausea, vomiting, confusion, dizziness, and hypersensitivity to light, sound, and touch.
Although herbicides are believed to be less toxic to mammals than other pesticides, they’re thought to be dangerous to the environment and other living organisms. For example, one type of herbicide called atrazine has been found to adversely affect frogs and other amphibians, hence its ban by the European Union (EU). Furthermore, persistent herbicides can contaminate groundwater and surface water.
Body systems affected by pesticides
According to Livestrong.com, many petroleum-based pesticides can cause neurological developmental issues among children, namely autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Exposure to pesticides during the important periods of brain development have been found to increase the instances of these conditions.
Pesticides can be dangerous to the endocrine system as well. A number of pesticides have been described as being able to mimic the effects of human estrogen and testosterone, making them endocrine disruptors. However, this has been observed largely in chronic exposure that took place over the course of several years.
Depending on the route of entry, pesticides can damage the various parts of the human body. For instance, consuming pesticides can harm the liver, kidney, spleen, and digestive system.
Items that can contain pesticides
Certain foods are contaminated with high levels of pesticide. As per DownToEarth.org, these are those foods, listed from most to least contaminated:
- Peaches
- Apples
- Sweet bell peppers
- Celery
- Nectarine
- Strawberries
- Cherries
- Kale
- Lettuce
- Imported grapes
- Carrots
- Pears
- Collard greens
- Spinach
- Potato
- Green beans
- Summer squash
- Peppers
- Cucumbers
- Raspberries
- Domestic grapes
- Plums
- Oranges
- Cauliflower
- Tangerines
- Mushrooms
- Bananas
- Winter squash
- Cantaloupes
- Cranberries
- Honeydew melons
- Grapefruits
How to avoid pesticides
There are a great number of ways to greatly reduce pesticide exposure. These include:
- Purchasing organic and locally grown fruits and vegetables
- Washing fruits and vegetables prior to eating. Be sure to thoroughly dry produce with a clean paper towel or cloth after washing. Use only cold tap water for this, and avoid soaps, bleaches, and detergents to minimize the risk of chemicals entering vegetables or fruits.
- Grow produce in a backyard garden, then make use of non-toxic methods to control pests. These can range from using traps and barriers to applying diatomaceous earth.
- Enforce a no-shoes policy in the home to decrease the amount of pesticide residue being left on carpets and floor surfaces.
Where to learn more
- Pesticides are heavily used near thousands of California schools
- Pesticides are one of top three ‘worst toxic pollution problems’ on planet, say non-profit groups
- Pesticides Cause Parkinson’s Disease
- Pesticides continue to contaminate US streams, USGS report says
- Pesticides in the home will raise your child’s risk of getting cancer
Summary
Pesticides are pest-controlling and pest-eliminating substances that can cause a wide array of health problems.
Some like organophosphates and carbomates can impede acetylcholinesterase and bring about vomiting, diarrhea, hypotension, and fatigue. Others like pyrethroids can cause allergic skin reactions. Organochlorines, meanwhile, can harm the environment and lead to light, touch, and sound hypersensitivity.
Pesticides are known to affect a multitude of body systems and organs, such as the endocrine system, brain, liver, kidneys, and digestive system.
Sources include:
ToxTown.NLM.NIH.gov
Healthline.com
Toxipedia.org
Livestrong.com
DownToEarth.org
Learn.EarthEasy.com
Tagged Under: