Bendiocarb – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/29/2017 / By Michelle Simmons

Bendiocarb is a member of a class of insecticides called carbamates. It is an insecticide that is applied on turf, soil, shrubs, trees, and ornamental plants used against different types of pests, such as beetles, aphids, mites, and caterpillars. In addition, this insecticide is made to be applied indoors, such as in houses, hotels, restaurants, warehouses, hospitals, railroad boxcars, and aircraft. It is used against spiders, wasps, ants, flies, and stored-product pests. Moreover, bendiocarb is also used as a seed treatment on sugar beets and maize to control snails and slugs. Products that use bendiocarb as an active ingredient are formulated as granules, dusts, or sprays. This insecticide works by interrupting the normal functioning of an insect’s nervous system, interfering with an enzyme necessary for normal nerve transmission and eventually resulting to the death of the targeted pest. It was first registered in the U.S. in 1980, but its registration was voluntarily canceled in September 1999. Eventually, all products that contain bendiocarb lost registration in December 2001. Bendiocarb has the molecular formula of C11H13NO4.

List of known side effects
Products that contain bendiocarb are low to moderate in toxicity, while in its pure form is highly toxic. It can be absorbed by the body through skin and eye contact, inhalation and ingestion. Bendiocarb can be toxic if inhaled and swallowed. Exposure to bendiocarb may cause gastrointestinal cramps, sweating, and restlessness. Since bendiocarb is a carbamate compound, like all carbamate pesticides, it can cause malaise, muscle weakness, dizziness, and sweating. It can also cause headache, salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. In addition, it can cause miosis with blurred vision, incoordination, muscle twitching, and slurred speech. Furthermore, in more serious cases, it may cause central nervous system depression such as coma, seizure, and hypotonicity, hypertension, cardiorespiratory depression, dyspnea, bronchospasms, and bronchorrhea with eventual pulmonary edema. It may also cause mild eye and skin irritation.
Bendiocarb can affect wildlife as it is highly toxic to birds, such as ducks and quails, honey bees, earthworms, and fish and aquatic invertebrates, such as shrimp, crabs, and insects.
Body systems affected by bendiocarb
Bendiocarb can adversely affect several body systems such as the digestive, respiratory, nervous, muscular, ocular, and integumentary system.
Items that can contain bendiocarb
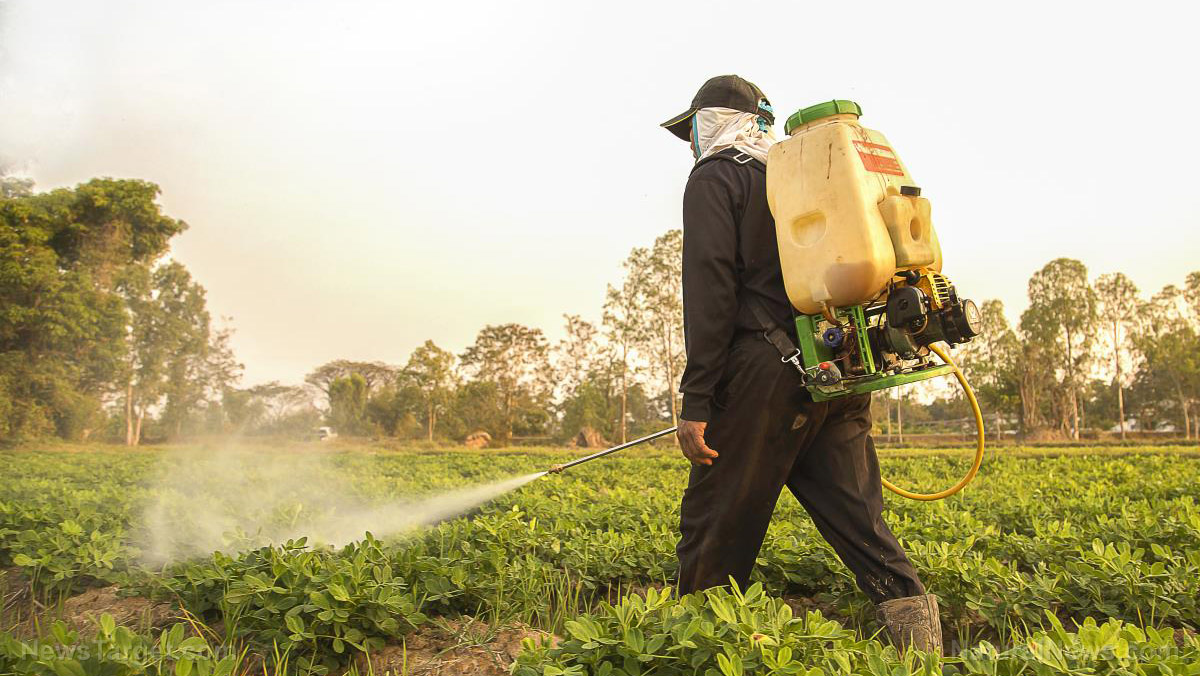
Bendiocarb can be found in insecticides that are used to control beetles, aphids, mites, caterpillars, spiders, wasps, ants, and flies and applied on non-cropped areas, such as paths and railroads, residences and commercial buildings, turf, and ornamentals. Some of the products that contain bendiocarb are Ficam, Dycarb, Rotate, Niomil, Turcam, Tattoo, Multamat, Multimet, Sudoxin, Seedox, and Garvox.
How to avoid bendiocarb
There are several ways to avoid bendiocarb when working with the chemical. One of these is to wear personal protective equipment made from chemical-resistant material, such as suits, gloves, footwear, and headgear, to avoid skin contact. Another way is to wear a direct vent goggles when airborne particles or dust are present. Moreover, respirators can be used – make sure it is used properly.
Where to learn more
Summary
Bendiocarb is a carbamate pesticide used against beetles, aphids, mites and caterpillars, and is applied on turf, soil, shrubs, trees and ornamental plants. It is also used to control spiders, wasps, ants, flies and stored-product pests in houses, hotels, restaurants, warehouses, hospitals, railroad boxcars and aircraft.
Bendiocarb may cause gastrointestinal cramps, sweating, and restlessness.
Bendiocarb may lead to carbamate poisoning that can cause headache, salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, miosis with blurred vision, incoordination, muscle twitching and slurred speech.
More severe cases of bendiocarb exposure may cause coma, seizure, hypotonicity, hypertension, cardiorespiratory depression, dyspnea, bronchospasms and bronchorrhea with eventual pulmonary edema.
Bendiocarb may irritate the skin and eyes.
Bendiocarb is extremely toxic to birds, honey bees, earthworms, fish, and aquatic invertebrates.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: