Linuron – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/29/2017 / By Zoey Sky

Linuron is a substituted urea herbicide used to control annual and perennial broadleaf and grassy weeds. Applied on both crop and non-crop sites, linuron works by inhibiting photosynthesis in target weed plants. It is labeled for field and storehouse use in crops like soybean, cotton, potato, corn, celery, parsnips, sorghum, asparagus, and carrots.
Linuron is a slightly toxic compound in the EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) toxicity class III. It is a General Use Pesticide (GUP), and labels for products containing linuron must bear the signal word CAUTION.
Linuron appears as an odorless, white crystalline solid. It is available in a variety of formulations such as wettable powders, emulsifiable concentrates, and suspension concentrates.
Linuron’s trade names and identifiers include:
- 56645-87-5 [RN]
- Afalon
- Afalon inuron
- Alfalon
- Aphalon
- Atlas linuron
- Cephalon [Wiki]
- Certroli-Lin
- D008044
- Du Pont 326
- EINECS 206-356-5
- Garnitan
- Herbicide 326
- Hoe 02 810
- Laroks [Polish]
- Linex [Wiki]
- Linex 4L
- Linorox
- Linurex
- LINURON-D6
- Lorex
- Lorox
- Lorox linuron weed killer
- Lorox Weed Killer
- Malurane
- Methoxydiuron
- MFCD00055249 [MDL number]
- Mudekan

List of known side effects
Linuron is harmful if swallowed, and it is suspected of causing cancer. The chemical may damage fertility or the unborn child. Linuron may cause damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
It can cause coughing and shortness of breath. Linuron can also cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, confusion, and electrolyte depletion. Exposure to the substance can also cause protein metabolism disturbances, moderate emphysema, and weight loss with chronic exposure.
Body systems affected by linuron
The systemic toxicity of linuron is unlikely unless large amounts have been ingested. Linuron can irritate the eyes, skin, and mucous membranes.
Items that can contain linuron
Linuron is a herbicide used for the pre- and post-emergence control of annual grass and broad-leaved weeds. It is used to control pests such as chickweed, prickly lettuce, lambsquarter, crabgrass, and goosegrass.
Linuron is applied on a wide variety of crops including asparagus, carrots, parsnips, beans, cereals. The herbicide is also applied on cotton, coffee, tea, rice, and ornamentals. Some products that use this active include Afalon 450 SC, Linuron 50SC, Blios, and Uranus.
How to avoid linuron
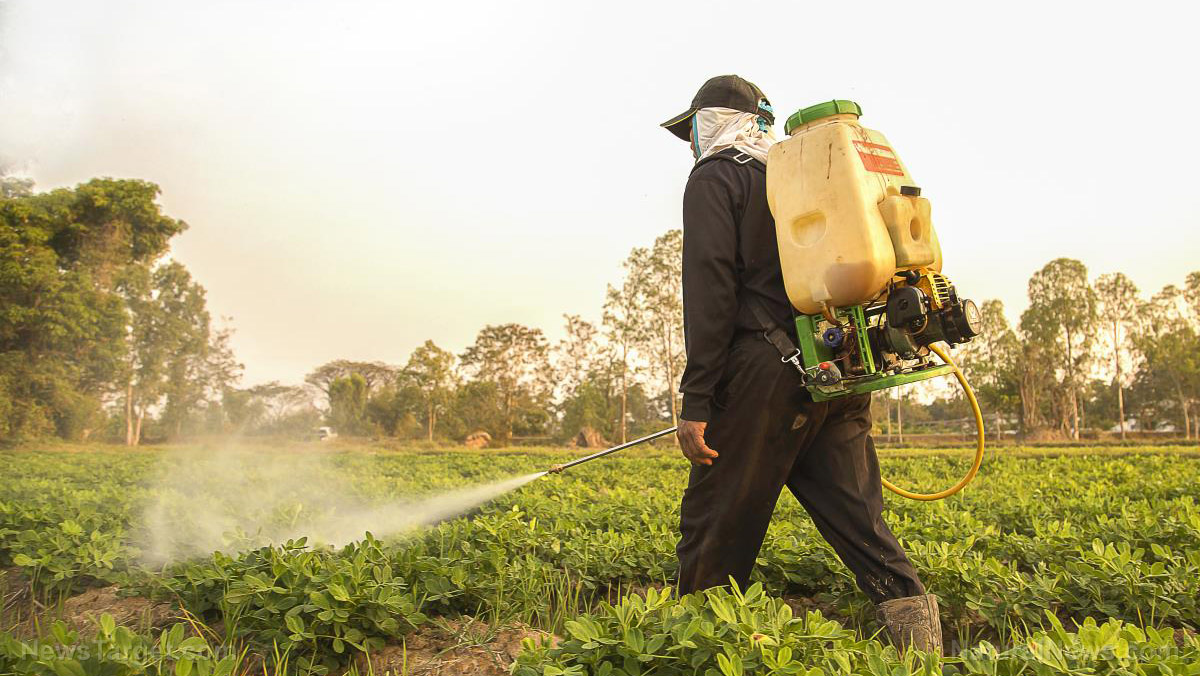
When handling linuron, always wear the proper protective gear.
- Respirator – Particulate. (AS/NZS 1716 & 1715, EN 143:2000 & 149:2001, ANSI Z88 or national equivalent)
- Eye – Safety glasses with side shields and chemical goggles.
- Hands/Feet – Wear chemical protective gloves, e.g. PVC. The suitability and durability of the glove type is dependent on usage. Important factors in the selection of gloves include frequency and duration of contact, chemical resistance of glove material, glove thickness, and dexterity. Select gloves tested to a relevant standard (e.g. Europe EN 374, US F739, AS/NZS 2161.1 or national equivalent). If prolonged or frequently repeated contact occurs, a glove with a protection class of 5 or higher (breakthrough time greater than 240 minutes according to EN 374, AS/NZS 2161.10.1 or national equivalent) is recommended. For brief contact, a glove with a protection class of 3 or higher (breakthrough time greater than 60 minutes according to EN 374, AS/NZS 2161.10.1 or national equivalent) is recommended. Wear gloves with clean hands and always replace contaminated gloves. After using gloves, hands should be washed and dried thoroughly. The application of a non-perfumed moisturizer is recommended.
- Other – Wear overalls and a PVC apron, apply barrier cream and skin cleansing cream, and always check if an eye wash unit is close by.
- Engineering controls – A local exhaust ventilation is required where solids are handled as powders or crystals; even when particulates are relatively large, a certain proportion will be powdered by mutual friction. Exhaust ventilation should be designed to prevent accumulation and re-circulation of particulates in the workplace.
Where to learn more
Summary
Linuron is a herbicide used to control annual and perennial broadleaf and grassy weeds.
Linuron is a slightly toxic compound in the EPA toxicity class III.
Linuron is harmful if swallowed, and it is suspected of causing cancer.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: