Sodium chlorate — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/29/2017 / By Zoey Sky

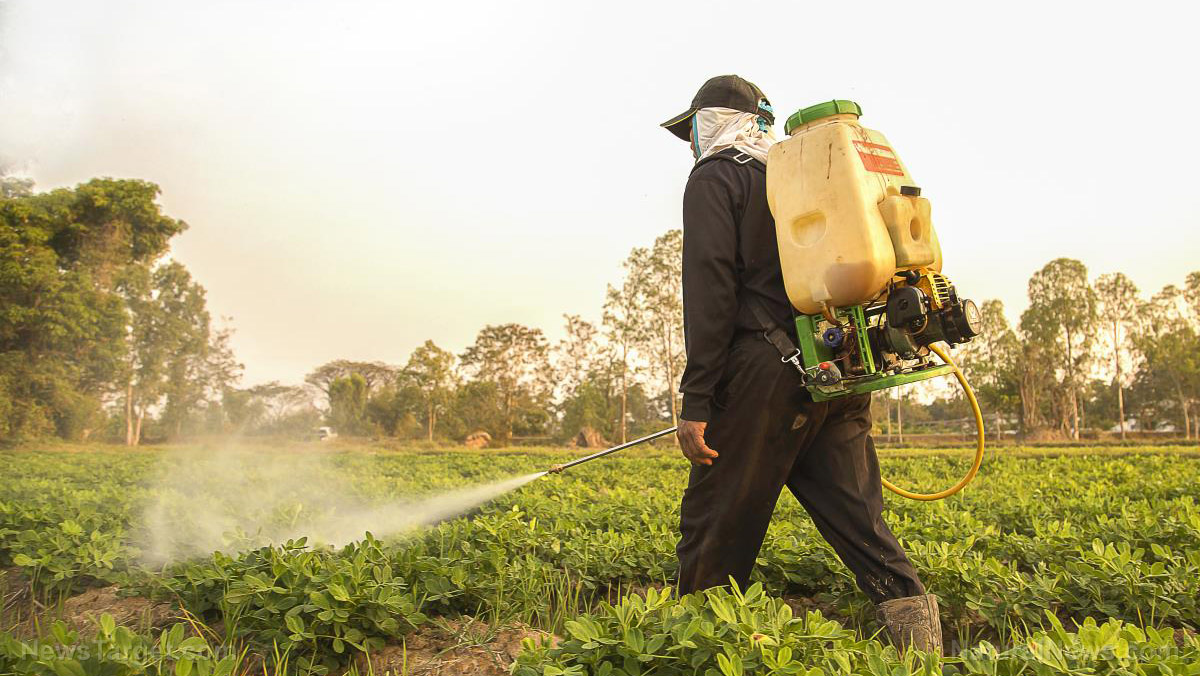
Sodium chlorate is a colorless solid used as a herbicide in both household weedkillers and professional agricultural products. In 2005, the use of sodium chlorate as a pesticide/fumigant was banned under the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, apart from quarantine and shipping uses. However, in March 2010, these uses were also banned because of its adverse effects.
Sodium chlorate is also known as 7775-09-9, Chloric acid, sodium salt, Asex, Polybor-chlorate, Chlorate de sodium, Chlorsaure, Tumbleleaf, Atlacide, Desolet, Kusatol, Rasikal, Sodakem, Chlorate salt of sodium, Dervan, Oxycil, Travex, Defol, and Fall.
An odorless pale yellow to white crystalline solid, sodium chlorate is appreciably soluble in water and heavier so it can sink and dissolve at a rapid rate. Although it is not itself flammable, the solid product and even 30 percent solutions in water are powerful oxidizing agents.
If sodium chlorate comes into contact with wood, organic matter, ammonium salts, sulfur, sulfuric acid, various metals, and other chemicals, it can result in fires or explosions, particularly if any solid materials are finely divided. Excessive heat, as in fires, may cause evolution of oxygen gas that may increase the intensity of fires and may also result in explosions. Mixtures with combustible materials are very flammable and may be ignited by friction.

List of known side effects
Sodium chlorate is a strong oxidizer. It is also harmful if swallowed. Sodium chlorate is toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects.
Ingestion of a toxic dose of sodium chlorate, at least 1/2 ounces (oz.), can cause severe gastroenteric pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. It can also cause respiratory difficulties/dyspnea, including failure of respiration. Kidney and liver injury may also be produced. The lethal oral dose for an adult is approximately 15 grams (gm).
Contact with sodium chlorate causes irritation of eyes and skin. The major cause of death from a lethal dose of sodium chlorate is acute renal failure.
Body systems affected by sodium chlorate
Sodium chlorate may affect blood cells and damage the kidneys. Acute exposure to the compound may also damage the liver and have negative effects on the respiratory system. The kidney tubules may be severely damaged without producing detectable methemoglobinemia.
Chronic exposure to sodium chlorate may cause a lack of appetite and weight loss. The prolonged chronic exposure to inhalation of sodium chlorate may cause mucous membrane irritation.
Items that can contain sodium chlorate
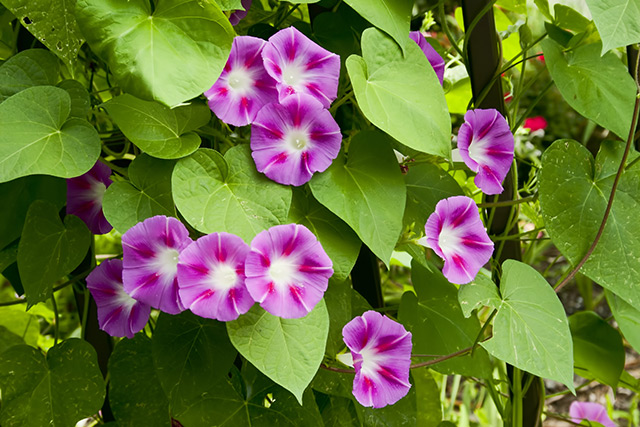
Sodium chlorate is a non-selective herbicide often used in non-cropping areas and for total vegetation clearance. It is used to control pests in total vegetation such as morning glory, Johnsongrass, St. John’s Wort, and Canada thistle.
Sodium chlorate is usually applied in non-cropped areas like roadsides, fence ways, and ditches. It is also used as a defoliant and desiccant for cotton, corn, flax, soybeans, sorghum, peas, beans, and rice.
Sodium chlorate is used for making herbicides, explosives, dyes, matches, inks, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, defoliants, paper, and leather.
How to avoid sodium chlorate
When handling sodium chlorate, make sure that you always wear the required safety gear.
- Eye – Chemical goggles and full face shield. Contact lenses pose a special hazard because soft lenses may absorb irritants and all lenses concentrate them.
- Hands/Feet – Wear chemical protective gloves (PVC), and wear safety footwear or safety gumboots (rubber). Gloves must only be worn on clean hands. After using gloves, hands should be washed and dried thoroughly.
- Other – Wear overalls/ PVC Apron. A PVC protective suit may be required if exposure severe. Eyewash unit. Ensure there is ready access to a safety shower.
Where to learn more
Summary
Sodium chlorate is as a herbicide used in both household weedkillers and professional agricultural products.
Sodium chlorate is used for making herbicides, pharmaceuticals, defoliants, and leather.
Acute exposure to sodium chlorate may have negative effects on the respiratory system.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: