Fenoprop – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
12/02/2017 / By Frances Bloomfield

Fenoprop, also known as 2-(2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy) propionic acid, is a herbicide and plant growth regulator commonly used on woody plants and broad-leaf weeds. It is used as industrial, commercial, and agricultural herbicide for rice, sugarcane, maize, orchards, pasture, rangeland, lawns, turf, and aquatic areas. Though once widely used in the U.S. or industrial, commercial, and agricultural purposes, it’s since been banned from use in 1985 due to the various health risks associated with this chemical.

List of known side effects
Fenoprop is a chlorophenoxy compound, so its use can increase the risk of chlorophenoxy compound poisoning. The symptoms of this condition include:
- Confusion
- Headache
- Increased heart rate
- Kidney failure
- Metabolic acidosis resulting in odd breath odor
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Inhaling fenoprop can be particularly dangerous. Apart from irritating the respiratory tract, fenoprop has been known to cause dizziness, coughing, burning sensations in the chest and nasopharynx, and incoordination.
Fenoprop is just as harmful when swallowed. The ingestion of large amounts of fenoprop have been known to cause:
- Acute lung injury
- Bradycardia
- Coma
- Emesis
- Fever
- Hypotension
- Miosis
- Mucosal ulcerations
- Renal failure
- Respiratory failure
- Tachycardia
Moreover, fenoprop can irritate the eyes and skin with direct contact. Prolonged or repeated exposure increase the risk of corneal injury.
Body systems affected by fenoprop
Fenoprop is an irritant of the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. It can be harmful to the liver and kidneys as well.
Items that can contain fenoprop
According to the Pesticide Properties DataBase, fenoprop can be found in a number of herbicides and has been marketed under a number of different brand names and synonyms. These include:
- Fruitone T
- Kuron
- Silvex
- Silvi-Rhap
- Chlorophenoxy herbicide
- Propanoic acid
Additionally, the following companies are believed to have been involved in the manufacturing and supplying of this chemical historically or actively:
- Dow Chemical Co.
- AmChem
- Rhone-Poulenc
- Vertac
How to avoid fenoprop
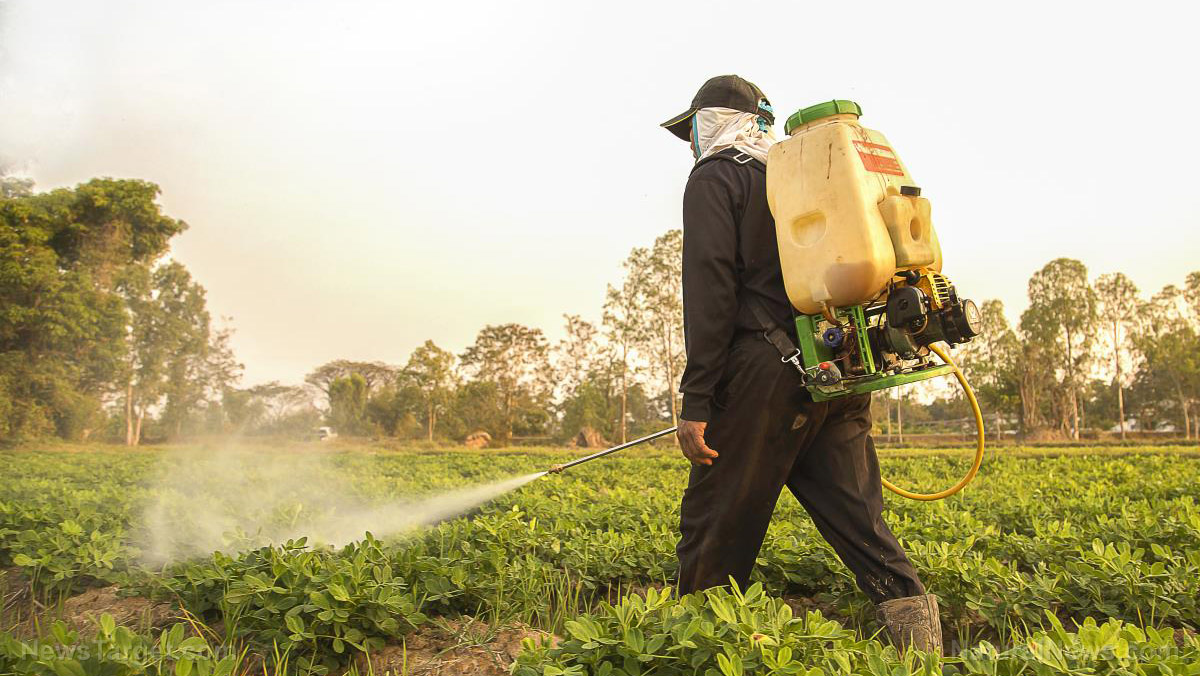
To prevent exposure to fenoprop, make it a point to wear the appropriate protective gear whenever handling this material. Chemical safety goggles, protective gloves, and respirators are recommended. For extra protection, keep fenoprop away from any sources of ignition or heat. These can cause fenoprop to emit gases containing carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
Where to learn more
Summary
Fenoprop is an herbicide that can be particularly dangerous when inhaled or ingested. Either can cause an individual to experience a wide array of symptoms, including but not limited to nausea, vomiting, fever, and increased heart rate. Fenoprop can irritate the skin and eyes too, and can cause liver and kidney damage over a certain period of time.
Sources include:
HazMap.NLM.NIH.gov
PesticideInfo.org
PubChem.NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov
ToxNet.NLM.NIH.gov
Sitem.Herts.AC.uk
FisherSci.com
Tagged Under: