Diuron – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
12/05/2017 / By Rita Winters

Diuron is a pre-emergence herbicide that is used to control a variety of annual and perennial broadleaf, grassy weeds and mosses. It targets bermudagrass, fathen, pigweed, charlock, sowthistle, wild radish, wild turnip, capeweed, deadnettles, poppies, and barnyard grass. Diuron, a colorless crystalline compound in pure form, works by inhibiting photosynthesis.
This chemical is moderately toxic to mammals, moderately toxic to birds, earthworms and aquatic species, but is highly toxic to algae. Other names and synonyms of diuron include N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl urea; 3-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea; 1-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,3-dimethyluree; N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)(dimethylamino)carboxamide; and 3-(3,1-dimethylureum.

List of known side effects
Diuron may cause poisoning in humans via the dermal, eye, inhalation, and ingestion routes of exposure. However, systemic toxicity is unlikely unless large amounts have been ingested. Some negative side effects of diuron exposure include irritation to the eyes, skin and mucus membranes; coughing and shortness of breath; nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, confusion and electrolyte depletion; protein metabolism disturbances, moderate emphysema and weight loss (when chronically exposed).
This chemical may also cause changes in blood chemistry, increased mortality growth retardation, abnormal blood pigment and anemia, as seen in animal tests in the laboratory. Some other symptoms show decreased body weight of offspring, wavy ribs, extra ribs, delayed bone formation, reproductive and embryotoxic effects. Other side effects include methemoglobinemia.
Water contamination may result in behavioral, biochemical, developmental and mortality of aqueous organisms such as amphibians, annelida, aquatic plants, cnidaria, crustaceans, echinoderms, fish, insects, molluscs, nematodes and flatworms, phytoplankton, terrestrial plants and zooplankton.
Body systems affected by diuron
Diuron poisoning may affect the central nervous system, respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. It is not mutagenic, a possible carcinogen, but is an endocrine disruptor, reproductive toxin and is teratogenic. Severe poisoning may result in enlargement of the liver and spleen.
Items that may contain diuron
Food items that may contain traces of diuron include vegetables such as asparagus, peas, pulses, fruit such as bananas and pineapples.
Other crops that may contain residue are cotton, lucerne, lupins, sugarcane; cereals like wheat barley, oats, triticale, tea; and ornamentals including tulips, daffodils and iris.
There are over 370 registered products that contain diuron, most of which are available in the country. The list includes names such as 20 mule team ureabor 8d improved formula; Acticide pm flowable; Bo-rid 10h-6.25k soil sterilant; Chemiuron 80% w.p. a diuron weed killer wettable powder; Dibro 1 granular weed killer; Helena brand diuron 80 wp weed killer; Monobor-chlorate granular d weed and grass killer; Sprakil sk-13 granular weed killer and many more.
How to avoid diuron
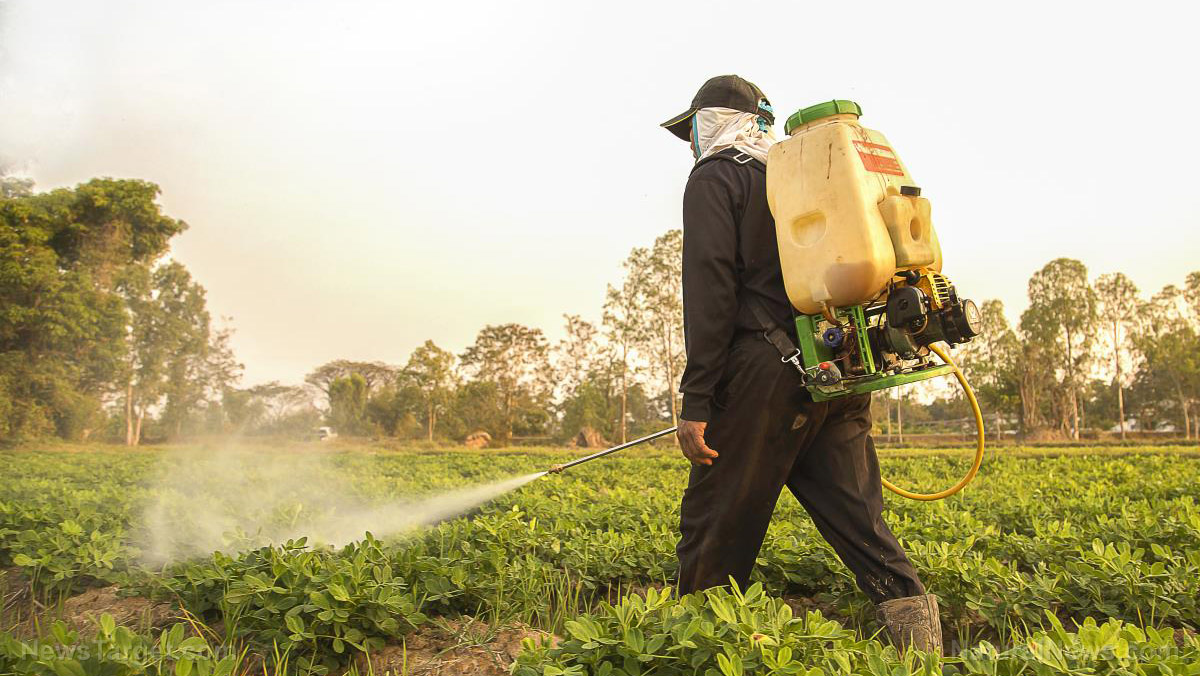
Diuron is a chemical herbicide used in commercial farms and other places with publicly-accessible flora (including parks). Avoid using chemicals that include diuron or any of its synonyms, or use minimally. It is not registered for use in residential areas, however, it is still being used by some individuals.
When handling toxic chemicals like diuron, always wear protective gear including chemical gloves, boots, coveralls, goggles or a full-face respirator. Personnel handling chemicals must undergo sufficient chemical-handling training and proper safety procedures. Prevent unauthorized personnel from accessing storage locations for chemical pesticides. Keep the chemicals under lock and key.
If dermal exposure happens, wash the affected area with soap and water. Eyes that are contaminated with dusts or aerosols must be flushed with clean, running water for at least ten minutes. In case of inhalation of dusts or aerosols, move the victim to an open area with fresh air. In case of ingestion, transport the victim to the nearest emergency department as soon as possible.
Where to learn more
- 3M named in massive contamination scheme that allegedly caused widespread cancer
- Poison.news
- Chemicals.news
- Pesticides.news
- Toxins.news
Summary
Diuron is an herbicide used in many plants.
Diuron is teratogenic, and may cause infertility.
Diuron can be fatal.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: