Boscalid — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
12/14/2017 / By Janine Acero
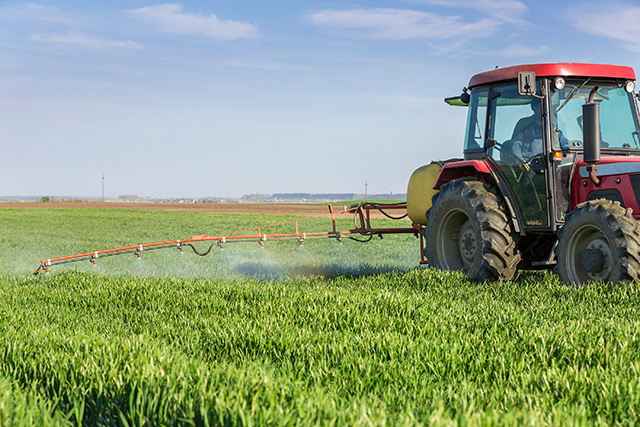

Boscalid is an agricultural fungicide active against a broad range of fungal pathogens such as alternaria blight, botrytis, powdery mildew, purple blotch, rust, leaf spot, target spot, brown spot, white mold, gray mold, stem rot and sclerotinia. It is applied to a variety of crops and vegetables including beans, brassicas, onions, garlic, shallots, peas, carrots, turnips; soybeans; fruits including grapes, apples, pears, strawberries; and tree nuts.
Boscalid is also used as a seed treatment and protectant. The pure compound is characterized as a white crystalline powder. It is often supplied as soluble granules which are mixed with water and applied as a spray. It has a molecular formula of C18H12Cl2N2O.

List of known side effects
Boscalid is not irritating to the eyes nor the skin. Exposure to boscalid may occur through inhalation and accidental ingestion of this compound at workplaces where boscalid is produced or used.
General side effects of chemical aspiration and ingestion include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Paleness
- Exhaustion
- Labored breathing
- Sore throat
- Coughing
- Wheezing
Non-persistent pesticides are considered less harmful for the environment, but boscalid may be toxic to aquatic organisms with long-term effects.
Body systems affected by boscalid
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classified boscalid as “suggestive evidence of carcinogenicity, but not sufficient to assess human carcinogenic potential.”
Boscalid has a low toxicity in animal studies. Boscalid generally caused side effects on the liver as well as on the thyroid.
Items that can contain boscalid
Boscalid may be found in related substances such as epoxiconazole, pyraclostrobin and fatty alcohol ethoxylate. In addition, some products like Filan, Signum, Splice, Tracker, Venture, Emerald, Bosco WG may contain boscalid as an active ingredient.
Manufacturers such as BASF and Goldengrass may supply such products historically or actively.
How to avoid boscalid
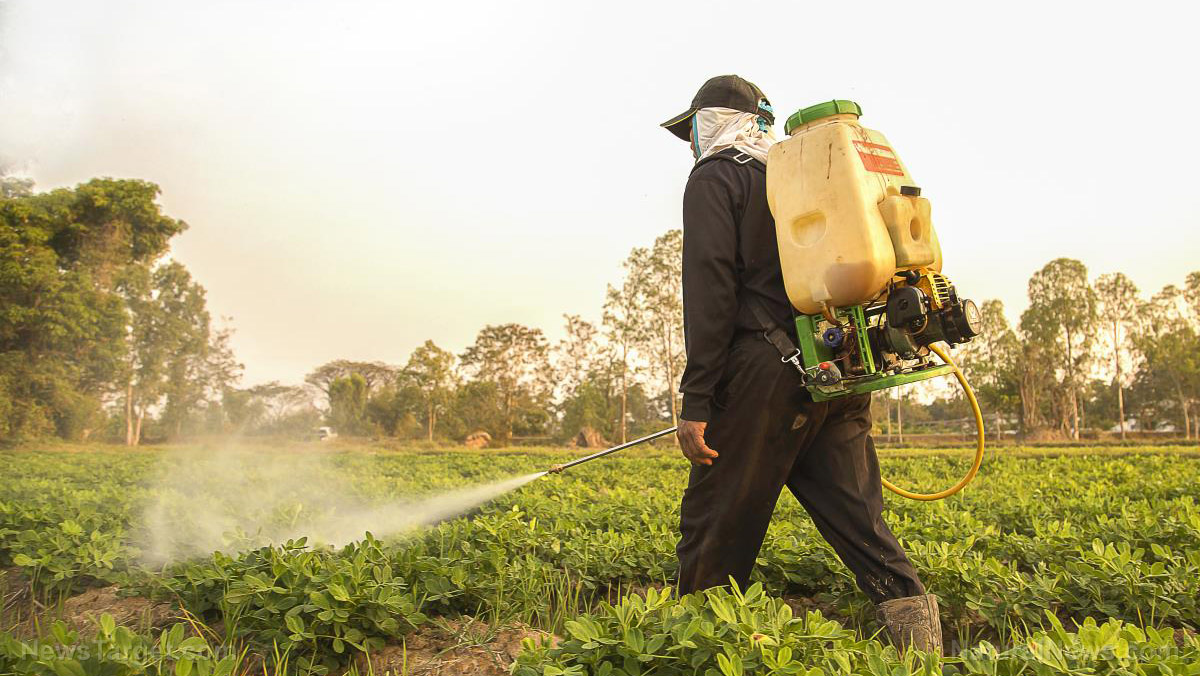
Handlers, mixers and applicators of boscalid may be exposed to its fumes, vapors and mists in the workplace. The following are some protective measures to avoid any contact with boscalid:
- Use this material only in well ventilated areas. In case of accidental aspiration, leave the area of contamination and go to an open area with fresh air or proper ventilation. Seek medical attention immediately.
- Avoid contact with skin or clothing. Wear a protective suit, chemical-resistant gloves and safety footwear or safety gumboots. Remove any contaminated clothing item carefully, avoiding any contact with the skin. Rinse the contaminated part of the skin with soap and water.
- Do not get this material in your eyes. Wearing goggles or a face shield is required before handling any chemical. In case of contact, remove contact lenses (if applicable), then rinse with running water for several minutes. Seek medical help at once.
- Do not eat, drink or smoke near this substance. In case of swallowing any amount of boscalid, give plenty of water to drink. Refer for medical attention immediately.
- Refer to the workplace regulations regarding proper handling of equipment before applying chemicals.
Where to learn more
Summary
Boscalid is an agricultural fungicide active against a broad range of fungal pathogens, which is applied to a variety of crops and vegetables. The pure compound is characterized as a white crystalline powder.
Boscalid has a low toxicity based on animal studies. It generally caused side effects on the liver and thyroid.
The EPA classified boscalid as “suggestive evidence of carcinogenicity, but not sufficient to assess human carcinogenic potential.”
Sources include:
Tagged Under: