Exploring the potential of using essential oils to control bipolaris leaf spot in maize
12/02/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
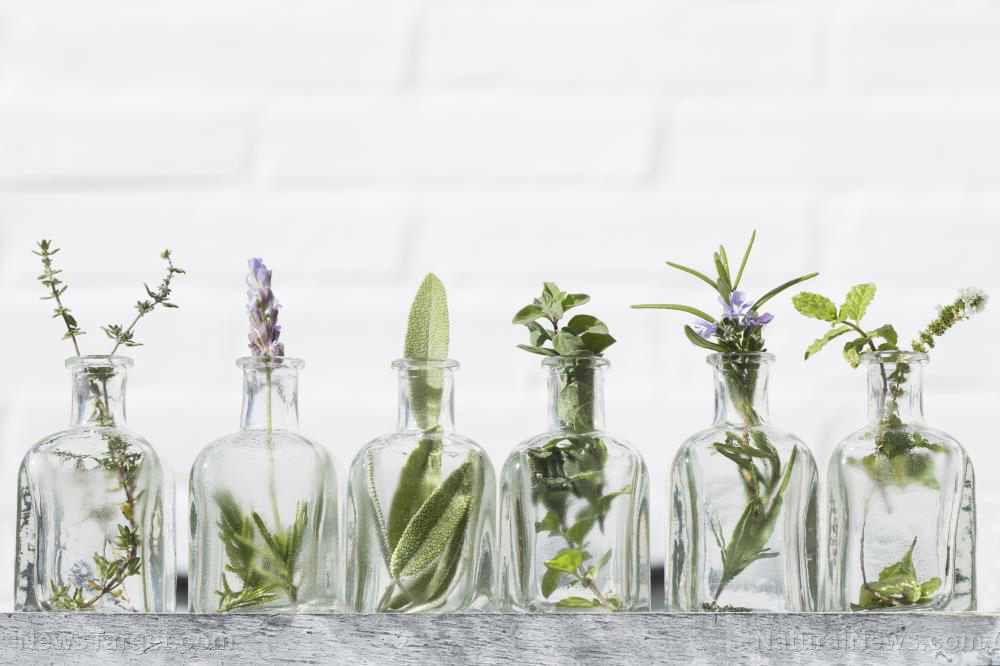

Researchers at the Federal University of Tocantins in Brazil evaluated the efficacy of essential oils derived from Ocimum pupuraceus, Cymbopogon nardus, Cymbopogon citratus and Lippia sidoides in inhibiting Bipolaris maydis mycelial growth and conidial germination. They reported their findings in an article published in the Journal of Medicinal Plants Research.
- Recently, research institutions have been emphasizing the use of alternative disease control agents because they offer beneficial effects on human and animal health as well as the ecosystem.
- Despite studies on botanical fungicides, their effective use requires knowledge about the applicability of natural products to different production systems.
- The researchers tested essential oils derived from different plants against the fungal pathogen, B. maydis that causes Southern corn leaf blight.
- They also analyzed the phytochemical composition of the oils using gas chromatography.
- Among the essential oils studied, L. sidoides essential oil 0.5 percent and 1 percent) effectively inhibited B. maydis mycelial growth and conidial germination.
- Thymol (92.68 percent) was found to be the main active component of L. sidoides essential oil.
- The researchers found that, at the concentration range of 0.75 to 3 percent, the oil was toxic to maize plants.
- They also observed lower values for the area under the curve of the bipolaris leaf spot when the essential oil (0.1 to 0.5 percent) was applied as a preventive agent prior to colonization of plant tissues by the pathogen.
- Treatment with L. sidoides essential oil (0.1 percent) reduced the severity of bipolaris leaf spot by 54 percent.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that L. sidoides essential oil can be used to prevent and treat bipolaris leaf spot in maize.
Read the full article at this link.
Journal Reference:
Dalmarcia DSCM, Micaele RDS, Joao VLDR, Talita PDSF, Pedro RAO, Eduardo RDS, Damiana BDS, Paulo HT, Fabrício SC, Gil RDS. FUNGISTATIC ACTIVITY OF ESSENTIAL OILS FOR THE CONTROL OF BIPOLARIS LEAF SPOT IN MAIZE. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research. 25 June 2019;13(12):280–287. DOI: 10.5897/jmpr2019.6781
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 PESTICIDES NEWS